From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For the geography and ecology of the WSMR area, see White Sands, New Mexico and Basin and Range Province.
|
White Sands Proving Ground (1945) Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range (1941)[2] |
|
|---|---|
| Part of United States Army | |
| New Mexico, Southwestern United States | |

Outline of WSMR at the Tularosa Basin
|
|
| Coordinates | 32°33′47″N 106°34′12″W |
| Built | 9 July 1945[3] |
| Built by | Ordnance Corps (United States Army)[3] |
| Open to the public |
WSMR Museum |
| Controlled by | Commanding General |
| Garrison | White Sands Missile Range Garrison Commander] |
| Current commander |
MG Gwen Bingham (2012–) [4] |
| Occupants |
|
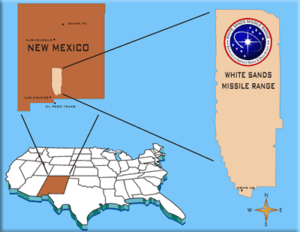 WSMR location |
|
|
||
Contents
Trinity test site
Public land grazing leases were canceled in December 1941 for the newly formed Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range. Robert Goddard transferred his rocket research group from Roswell, New Mexico to Annapolis, Maryland in July 1942. The Trinity (nuclear test) site was selected in November 1944; and the first atomic bomb was detonated at the Trinity test site on 16 July 1945.[7] The Trinity Site was declared a National Historic Landmark district on 21 December 1965,[8][9] and listed on the National Register of Historic Places on 15 October 1966.[10]V-2 rockets
Main article: V-2 sounding rocket
The first of 300 railroad cars of V-2 rocket components began to arrive at Las Cruces, New Mexico in July 1945 for transfer to WSPG.[11]:246
Launch Area 1 Army blockhouse (Launch Complex 33) was completed in
September. In November General Electric employees began to identify,
sort, and reassemble V-2 rocket components in Building 1538, designated
as Assembly Building 1. German rocket scientists of Operation Paperclip arrived at Fort Bliss in January 1946 to assist the V-2 rocket testing program.[7] After a static test firing of a V-2 engine on 15 March 1946, the first V-2 rocket launch
from Launch Complex 33 was on 16 April 1946. Approximately two V-2
launches per month were scheduled from Launch Complex 33 until the
German rocket scientists transferred from Fort Bliss to Redstone Arsenal
in 1949. Remaining V-2 rockets were launched from Launch Complex 33 on a
reduced frequency until 1952. Launch Complex 33 was designated a National Historic Landmark on 3 October 1985.[12][13] Refurbished Mittelwerk V-2 rocket #FZ04/20919 was returned to the WSMR Museum in May 2004 after being taken to the Kansas Cosmosphere and Space Center in September 2002 for restoration.Current operations
- At White Sands Test Facility (WSTF), Ground Support for the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) network of communications satellites
- At WSTF, Solar Dynamics Observatory – SDO ground station consists of two dedicated (redundant) 18-meter (59 ft) radio antennas at White Sands.
- Orion Project Launch Abort Flight Test Complex
- Missile testing and range recovery operations[14]
Chronology
- 1941, 13 April: Alamogordo Army Airfield established.[7]
- 1941, December: Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range established.
- 1944, February: Major General Gladeon M Barnes, chief of the Technical Division of the Office of Chief of Ordnance in Washington, sent teams of the War Department and the Ordnance Department of the Corps of Engineers to look for a US site for missile research.[15]:389
- 1945, 20 February: The Secretary of War approved the establishment of White Sands Proving Ground.[15]:290[11]:246
- 1945, Spring: Private F test firing[16]
- 1945, 25 June: Drilling of water wells began construction of WSPG facilities.[7]
- 1945, September: Launch Area 1 Army blockhouse (Launch Complex 33) was completed.[7]
- 1945, 26 September – 25 October: First test firing of the WAC-Corporal at WSPG.[11]:253
- 1948, 14 January: Alamogordo Army Airfield officially renamed Holloman Air Force Base.[7]
- 1953, June: USS Desert Ship (LLS-1) (Launch Complex 35) was built to test the Navy RIM-8 Talos missile.[7]
- 1958, 1 May: White Sands Proving Ground officially renamed White Sands Missile Range.[7]
- 1959: Shavetail rocket tested.
- 1963—1966: Little Joe II Apollo program launch escape system tests at WSMR Launch Complex 36[17]
- 1982: Space shuttle STS-3 landed at WSMR
- 1983—1993: The Simtel shareware archive was hosted at WSMR on ARPANET
- 2004: The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics named the WSPG a Historic Aerospace Site.[18]
- 2007, 14 November: NASA and a handful of community representatives broke ground at the Launch Complex-32 site for the Orion Abort Flight Test Launch Complex.[19][20]
Gallery

1945, the Trinity explosion, 0.016 seconds after detonation.


No comments:
Post a Comment