



















HAL Tejas
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Tejas | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| India's Light Combat Aircraft | |
| Role | Multirole fighter |
| National origin | India |
| Manufacturer | Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) |
| Design group | Aeronautical Development Agency |
| First flight | 4 January 2001 |
| Introduction | 20 December 2013[1] |
| Status | In production |
| Primary users | Indian Air Force Indian Navy |
| Number built | 14 (including prototypes as of December 2013)[2] |
| Program cost | US$1.2 billion[3] |
| Unit cost | |
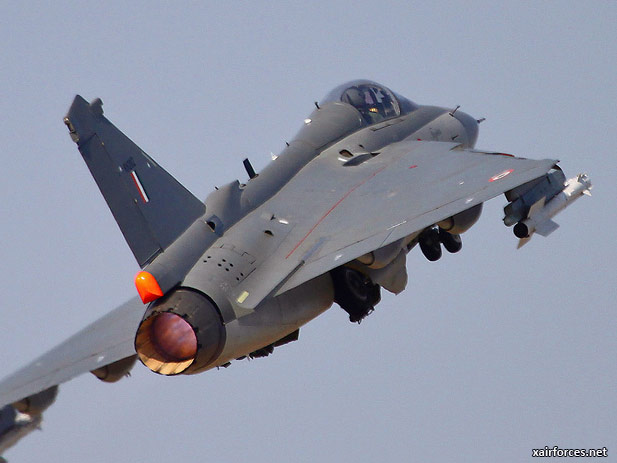
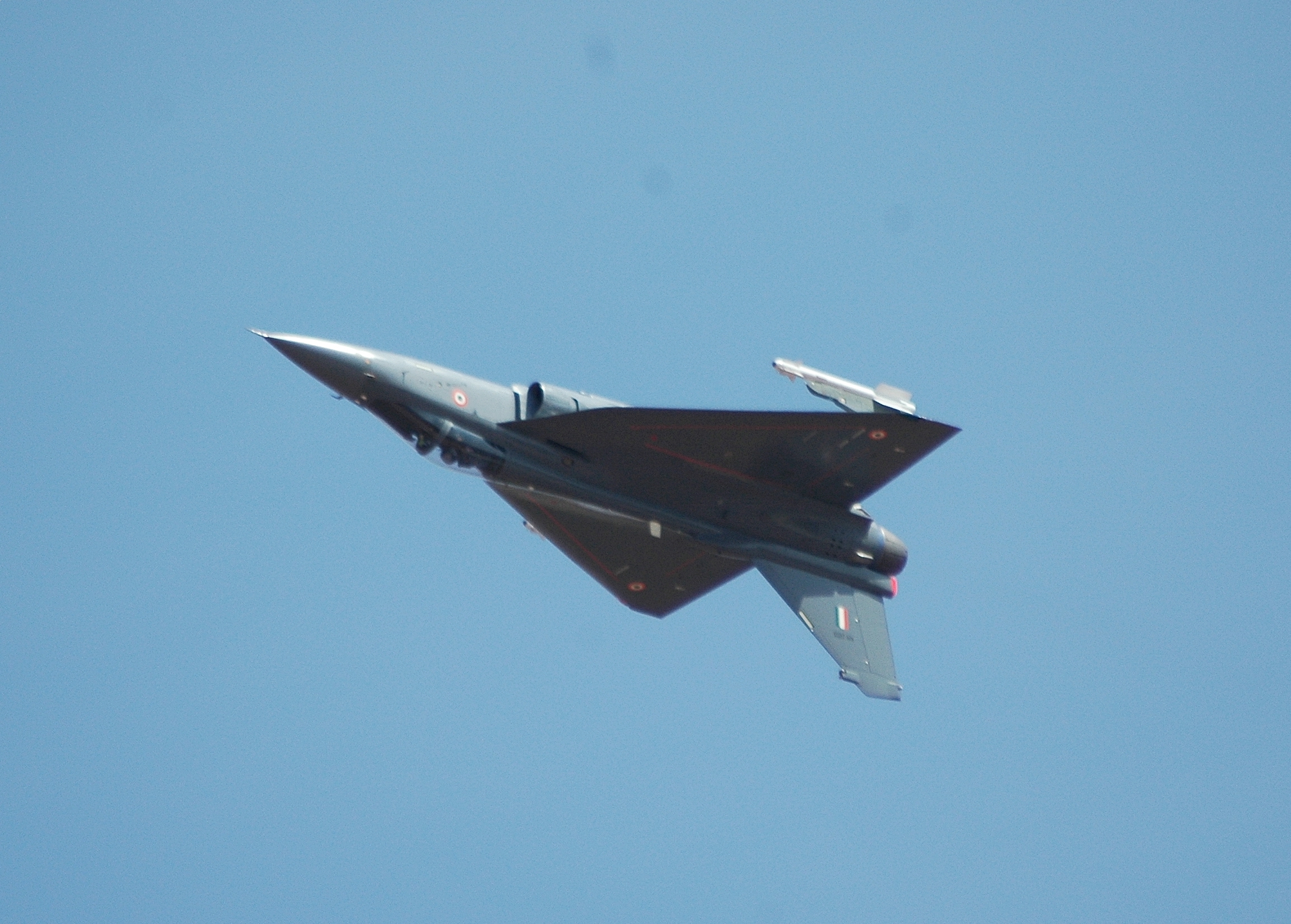
Tejas has a pure delta wing configuration, with no tailplanes or foreplanes, and a single dorsal fin. It integrates technologies such as relaxed static stability, fly-by-wire flight control system, multi-mode radar, integrated digital avionics system, composite material structures, and a flat rated engine. It is supersonic and highly manoeuvrable, and is the smallest and lightest in its class of contemporary combat aircraft.[8][9]
The Tejas is the second supersonic fighter developed indigenously by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) after the HAL Marut. The Indian Air Force (IAF) was reported to have a requirement for 200 single-seat and 20 two-seat conversion trainers, while the Indian Navy might order up to 40 single-seaters to replace its Sea Harrier FRS.51 and Harrier T.60.[10] The Tejas was cleared in January 2011 for use by Indian Air Force pilots. It received the second of three levels of operational clearance on 20 December 2013.[11][12]
Contents
Development
See also: Timeline of HAL Tejas
LCA programme
In 1983, IAF realised the need of an indigenous combat aircraft for two primary purposes. The principal and most obvious goal was the development of a replacement aircraft for India's ageing MiG-21 fighters. The MiG-21 has been the mainstay of the Indian Air Force since the 1970s. The "Long Term Re-Equipment Plan 1981" noted that the MiG-21s would be approaching the end of their service lives by the mid-1990s, and that by 1995, the IAF would lack 40% of the aircraft needed to fill its projected force structure requirements.[15]
The LCA programme's other main objective was to serve as the vehicle for an across-the-board advancement of India's domestic aerospace industry.[16] The value of the aerospace "self-reliance" initiative is not simply the production of an aircraft, but also the building of a local industry capable of creating state-of-the-art products with commercial spin-offs for a global market. The LCA program was intended in part to further expand and advance India's indigenous aerospace capabilities.[17]
To better accomplish these goals, the government chose to take a different management approach, and in 1984 established the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) to manage the LCA programme. Although the Tejas is most often described as a product of Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), responsibility for the development of the Tejas actually belongs to ADA, a national consortium of over 100 defence laboratories, industrial organisations, and academic institutions with HAL being the principal contractor.[18]
The Indian government's "self-reliance" goals for the LCA include indigenous development of the three most sophisticated — and hence most challenging — systems: the fly-by-wire (FBW) flight control system (FCS), multi-mode pulse-doppler radar, and afterburning turbofan engine.[19]
Of the five critical technologies the ADA identified at the beginning of the LCA programme as needing to be mastered for India to be able to design and build a "completely indigenous" fighter, two have been entirely successful: the development and manufacture of advanced carbon-fibre composite (CFC) structures and skins and a modern "glass cockpit." In fact, ADA has had a profitable commercial spin-off in its Autolay integrated automated software system for the design and development of 3-D laminated composite elements (which has been licensed to both Airbus and Infosys).[19] These successes have gone mostly unnoticed in the shadow of the problems encountered with the other three key technology initiatives. Nonetheless, as a result of the accomplishments of India's domestic industries, about 70% of the components in LCA are manufactured in India and the dependence on imported components used would be progressively reduced in the coming years.[20]
HAL serves as the prime contractor and has leading responsibility for LCA design, systems integration, airframe manufacturing, aircraft final assembly, flight testing, and service support.[18] The ADA itself has primary responsibility for the design and development of the LCA's avionics suite and its integration with the flight controls, environmental controls, aircraft utilities systems management, stores management system, etc.
The IAF's Air Staff Requirement for the LCA were not finalised until October 1985. This delay rendered moot the original schedule which called for first flight in April 1990 and service entry in 1995; however, it also proved a boon as it is gave the ADA time to better marshal national R&D and industrial resources, recruit personnel, create infrastructure, and to gain a clearer perspective of which advanced technologies could be developed indigenously and which would need to be imported.[14][22]
Out of a total of 35 major avionics components and line-replaceable units (LRUs), only three involve foreign systems.[23] These are the multi-function displays (MFDs) by Sextant (France) and Elbit (Israel),[24] the helmet-mounted display and sight (HMDS) cueing system by Elbit,[24] and the laser pod supplied by Rafael (Israel).[25] However, even among these three, when the LCA reaches the production stage, the MFDs are expected to be supplied by Indian companies. A few other important items of equipment (such as the Martin-Baker ejection seat) have been imported.[23] As a consequence of the embargo imposed on India after its nuclear weapons tests in May 1998, many items originally planned to be imported were instead developed indigenously. The nuclear test sanctions delayed the development of technologies that were already many years behind schedule.[23]
Development history
Project definition commenced in October 1987 and was completed in September 1988. Dassault Aviation of France was hired as a consultant to review the PD and provide advice based on its extensive aviation expertise.[22] The phase costed
Phase 1 commenced in April 1993,[15] and focused on "proof of concept" and comprised the design development and testing (DDT) of two technology demonstrator aircraft which were named as TD-1 and TD-2. This would be followed by the production of two prototype vehicles (PV-1 and PV-2), TD-1 finally flew on 4 January 2001.[27] FSED Programme Phase-I was successfully completed in March 2004 and costed
Phase 2 commenced in November 2001,[15] and consisted of the manufacturing of three more prototype vehicles (PV-3, PV-4 and PV-5), leading to the development of the final variant that would join the air force and the navy and 8 Limited Series Production (LSP) aircraft, and establishment of infrastructure for producing 8 aircraft per year.[27] The phase costed
One of the most ambitious requirements for the LCA was the specification that it would have "relaxed static stability" (RSS). Although Dassault had offered an analogue FCS system in 1988, the ADA recognised that digital flight control technology would soon supplant it.[19] RSS technology was introduced in 1974 on the General Dynamics F-16 prototype, which became the first production aircraft to be slightly aerodynamically unstable by design, to improve manoeuvrability.[28] Most aircraft are designed with positive static stability, which induces aircraft to return to straight and level flight attitude if the pilot releases the controls; this reduces manoeuvrability as the inherent stability has to be overcome. Aircraft with negative stability are designed to deviate from controlled flight and thus be more manoeuvrable.[29][30]
Fly-by-wire flight control system has become state of the art technology.[31] Therefore, in 1992 the LCA National Control Law (CLAW) team was set up by the National Aeronautics Laboratory to develop India's own version for the Tejas.[32] However, Lockheed Martin's involvement was terminated in 1998 as part of an embargo enacted by the U.S. in response to India's second nuclear tests in May of that year.[33][34]
The NAL's CLAW team eventually managed to successfully complete integration of the flight control laws indigenously, with the FCS software performing flawlessly for over 50 hours of pilot testing on TD-1, resulting in the aircraft being cleared for flight in early 2001. The automatic flight control system (AFCS) of the Tejas has been highly praised by all of its test pilots, one of whom said that he found it easier to take off with the LCA than in a Mirage 2000.[35]
The LCA's maiden flight was made by TD-1 from National Flight Test Centre (NFTC), near Bangalore, on 4 January 2001,[27] and its first successful supersonic flight followed on 1 August 2003.[36] TD-2 made its first flight on 6 June 2002.[37] Pilots regarded the Tejas as the IAF's most "pilot friendly" fighter. An NFTC test pilot during the IOC ceremony on December 20, 2013 said: "As a multi-role fighter, the Tejas is at least the equal of the IAF's upgraded Mirage-2000. It can more than hold its own in our operational scenario."[38] Another IAF pilot said that the Tejas is better than the MiG-21.[39]
Another critical technology area tackled for indigenous development by the ADA team is the Multi-Mode Radar (MMR). It was initially planned for the LCA to use the Ericsson Microwave Systems PS-05/A I/J-band multi-function radar,[40] which was developed by Ericsson and Ferranti Defence Systems Integration for the Saab JAS 39 Gripen.[41] However, after examining other radars in the early 1990s,[41] The Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) became confident that indigenous development was possible. HAL's Hyderabad division and the LRDE were selected to jointly lead the MMR program and the radar development effort began in 1997.[43]
The DRDO's Centre for Airborne System (CABS) is responsible for running the test programme for the MMR. Between 1996 and 1997, CABS converted the surviving HAL/HS-748M Airborne Surveillance Post (ASP) into a testbed for the avionics and radar of the LCA.[44]
By mid-2002, development of the MMR was reported to be experiencing major delays and cost escalations. By early 2005 only the air-to-air look-up and look-down modes — two very basic modes — were confirmed to have been successfully tested. In May 2006 it was revealed that the performance of several modes being tested still "fell short of expectations."[45] As a result, the ADA was reduced to running weaponisation tests with a weapon delivery pod, which is not a primary sensor, leaving critical tests on hold. According to test reports, the crux of the problem is a serious compatibility issue between the radar and the advanced signal processor module (SPM) built by the LRDE. Acquisition of an "off-the-shelf" foreign radar is an interim option being seriously considered.[43][46][47]
Engine and propulsion
Initially, it was decided to equip the prototype aircraft with the General Electric F404-GE-F2J3 afterburning turbofan engine. Simultaneously, in 1986, a parallel programme to develop an indigenous powerplant was also launched.[48] In 1998, following India's nuclear tests, US placed sanctions on the sale of General Electric F404 turbofans. It was decided to invest in a domestic jet engine as a replacement of the F404. Cost overruns and Delays were encountered while developing the new Kaveri engine. After the lift of sanctions, decision was made to buy additional F404 engines for use on the initial Tejas production aircraft.[33] Led by the Gas Turbine Research Establishment, the GTRE GTX-35VS, named "Kaveri", was expected to replace the F404 on all production aircraft.[49]However, progress in the Kaveri development programme was slowed by technical difficulties. Development snags with the Kaveri resulted in the 2003 decision to procure the uprated F404-GE-IN20 engine for the eight pre-production LSP aircraft and two naval prototypes. General Electric was awarded a US$105 million contract in 2004 for development engineering and production of 17 -IN20 engines,[50] delivery of which began in 2006.[51] The F404-GE-IN20 was trial-installed on the Tejas and the engine generated more than 19,000 pounds (85 kN) uninstalled thrust and completed 330 hours of Accelerated Mission testing, equivalent of 1,000 hours of flight operation.[51] In 2007, an additional 24 F404-IN20 afterburning engines were ordered to power the first operational squadron of Tejas fighters.[50]
In mid-2004, the Kaveri failed its high-altitude tests in Russia, ending the last hopes of introducing it with the first production Tejas aircraft.[51][N 4] In February 2006, the ADA awarded a contract to the French aircraft engine company Snecma for technical assistance in working out the Kaveri's problems.[10] The Kaveri engine based on Snecma's new core, an uprated derivative of the M88-2 engine that powers the French Rafale fighter, providing 83–85 kilonewtons (kN) of maximum thrust was being considered a third option by DRDO. This led the IAF to object that since Snecma had already developed the core of the engine, the DRDO will not be participating in any joint development but merely providing Snecma with an indigenous stamp.[52]
In 2008, it was announced that the Kaveri would not be ready in time for the Tejas, and that an in-production powerplant would have to be selected in the 95 to 100 kilonewton (kN) (21,000–23,000 lbf) range to allow the aircraft to perform combat manoeuvres with optimal weapons load. The contenders were the Eurojet EJ200 and the General Electric F414.[53][54] IAF sources said that the airframe will have to be redesigned to accommodate the heavier engine, which is to take up to three-four years.[55]
After evaluation and acceptance of the technical offer provided by both Eurojet and GE Aviation, the commercial quotes were compared in detail and GE Aviation was declared as the lowest bidder. The deal will cover purchase of 99 GE F414 engines. The initial batch will be supplied by GE and the remainder will be manufactured in India under a transfer of technology arrangement.[56][57]
Initial production, further testing
On 25 April 2007, the first Limited Series Production (LSP-1) Tejas accomplished maiden flight, achieving a speed of Mach 1.1 (837.3 mph; 1,347.5 km/h).[22] The Tejas completed 1,000 test flights by 22 January 2009[22] with more than 530 hours of in-flight testing.[61] The Tejas achieved a speed of over 1,350 kilometres per hour (840 mph) during its sea level flight trials in 2009.[62] These trials were conducted at INS Hansa, Goa.[22] On 16 June 2008, LSP-2 made its first flight.[22]
On 23 April 2010, the third production aircraft (LSP-3) flew with a hybrid version of the Elta EL/M-2032 multi-mode radar,[22][63] and by June 2010, the fourth production aircraft (LSP-4) took first flight[22] in the configuration it would be delivered to the Indian Air Force in.[64]
By June 2010, the Tejas had also completed the second phase of hot weather trials. The objective of the hot weather trials was to prove that the aircraft was in an IOC configuration with the weapon system and sensors integrated.[65] The sea trials of the aircraft are also being carried out.[66] LSP-5 with IOC standard equipment took to skies on 19 November 2010.[67]
The trainer variant prototype took to the skies in November 2009.[68] In December 2009, the Indian government sanctioned
In November 2010, it was reported that the Tejas Mk1 reportedly fell short of the relaxed Air Staff Requirements stipulated for limited series production (LSP) aircraft. The areas that did not meet requirements were power to weight ratio, sustained turning rate, maximum speeds at low altitudes, AoA range, and weapon delivery profiles. The extent of the deficiencies was classified.[71]
Initial Operating Clearance (IOC) for the Tejas was awarded on 10 January 2011 by Defence Minister A K Antony to Chief of Air Staff Air Chief Marshal P V Naik. IOC allows IAF pilots to use the aircraft. The IAF plans to raise the first squadron in Bengaluru to iron out issues with ADA and HAL, and eventually base these fighters at Sulur Air Force Station, Coimbatore in the southern state of Tamil Nadu.[59][72][73][74]
The weapon tests including bombing begun in September 2011 at Pokhran range, to be followed by missile firing tests at Goa.[75] RAFAEL's Derby fire-and-forget missile will serve as the Tejas' initial medium range air-air armament.[76]
Tejas' Final Operational Clearance (FOC) was reportedly delayed from December 2012 until mid-2013 or later.[77][78] The Tejas program has enlisted EADS to help expand the flight envelope to meet service requirements.[79]
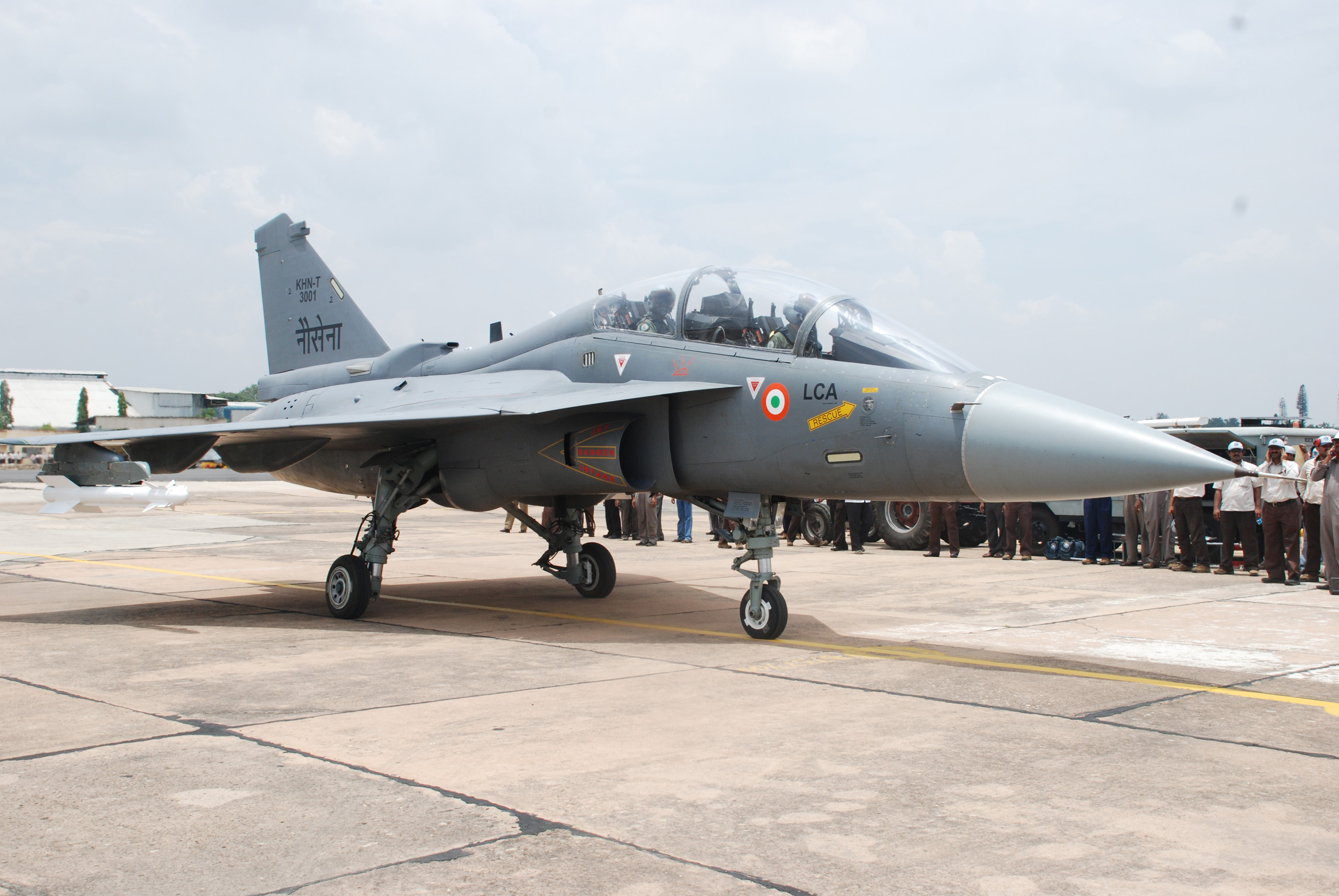
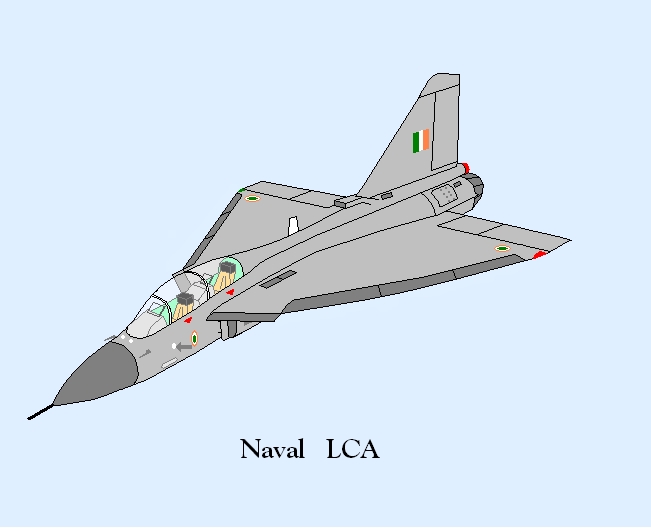
On 9 March 2012, LSP-7 took to its maiden flight from HAL airport.[22] The Naval LCA made its first flight, almost two years after being rolled out, on 27 April 2012.[80]
On 27 June 2012, three HAL Tejas (LSP 2, 3 and 5) aircraft completed precision bombing runs in the desert of Rajasthan, where they deployed a series of weapons, including laser-guided 1,000 lb bombs and unguided bombs. The LCA had conducted similar bombing runs in the month of September 2011 at Pokhran.[81] The Tejas had completed 1,941 flights by July 2012.[82] Some defence sources indicate that it will not reach FOC and become fully combat capable until 2015.[83]
The Tejas was grounded for over three months in the later half of 2012 because new helmets for the pilots extended above the ejection seats. The helmets could have prevented a smooth ejection by hitting the canopy before it was blown off, and represented a serious safety issue, hence flight testing was stopped in August 2012. The ejection systems were modified to rectify this issue, and flight tests resumed in November.[84] LSP 8 had a successful maiden test flight on 31 March 2013,[85] and the program had completed 2,418 test flights by 27 November 2013.[82][86] On 31 March 2013, LSP-8 took to its maiden flight from HAL airport.[22]
Operational clearance
HAL was instructed by the Indian government to strictly adhere to deadlines to ensure IOC-2 by the end of 2013 and Final Operational Clearance (FOC) by the end of 2014.[87] On 20 December 2013, the Initial Operational Clearance-II of the aircraft was issued, after which it was cleared to be flown by regular pilots of the Indian Air Force and begin induction into squadron service. The first squadron of 18 to 20 fighters will be based at Sulur Air Force Station in the state of Tamil Nadu,[88] and it will work to achieve Final Operational Clearance (FOC) by December 2014.[89] To fulfill the IOC-II standard, the aircraft was certified to carry close to three tons of weapons which include laser-guided 500 kg bombs and short-range R-73 missiles,[90][91] reach top speeds of 1,350 km per hour, withstand turns up to 7g, reach angle of attack of 24 degrees (from 17 degrees initially), and have an operational radius of 400–500 km. Cost of a single unit in the IOC-2 configuration is betweenTo obtain FOC, the fighter will have to be certified for six more criteria. Integration of Derby and Python BVR missiles weighing 150 kg, with a range of 70 km, as well as a Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23 gun will be undertaken. An air-to-air refuelling probe supplied by Cobham will be added. The angle of attack will be increased from 24 to 28 degrees,[92] the braking system will be enhanced, and the existing nose cone radome made of composites will be replaced by a quartz model to increase the current radar range of 45–50 km to more than 80 km. These modifications are expected to be completed within 15 months of IOC-II.[89][94]
In 2014 the FOC was pushed back as multiple aircraft would need to be tested and the only one produced to date would need further modifications to complete all tests.[95]
Design
Overview
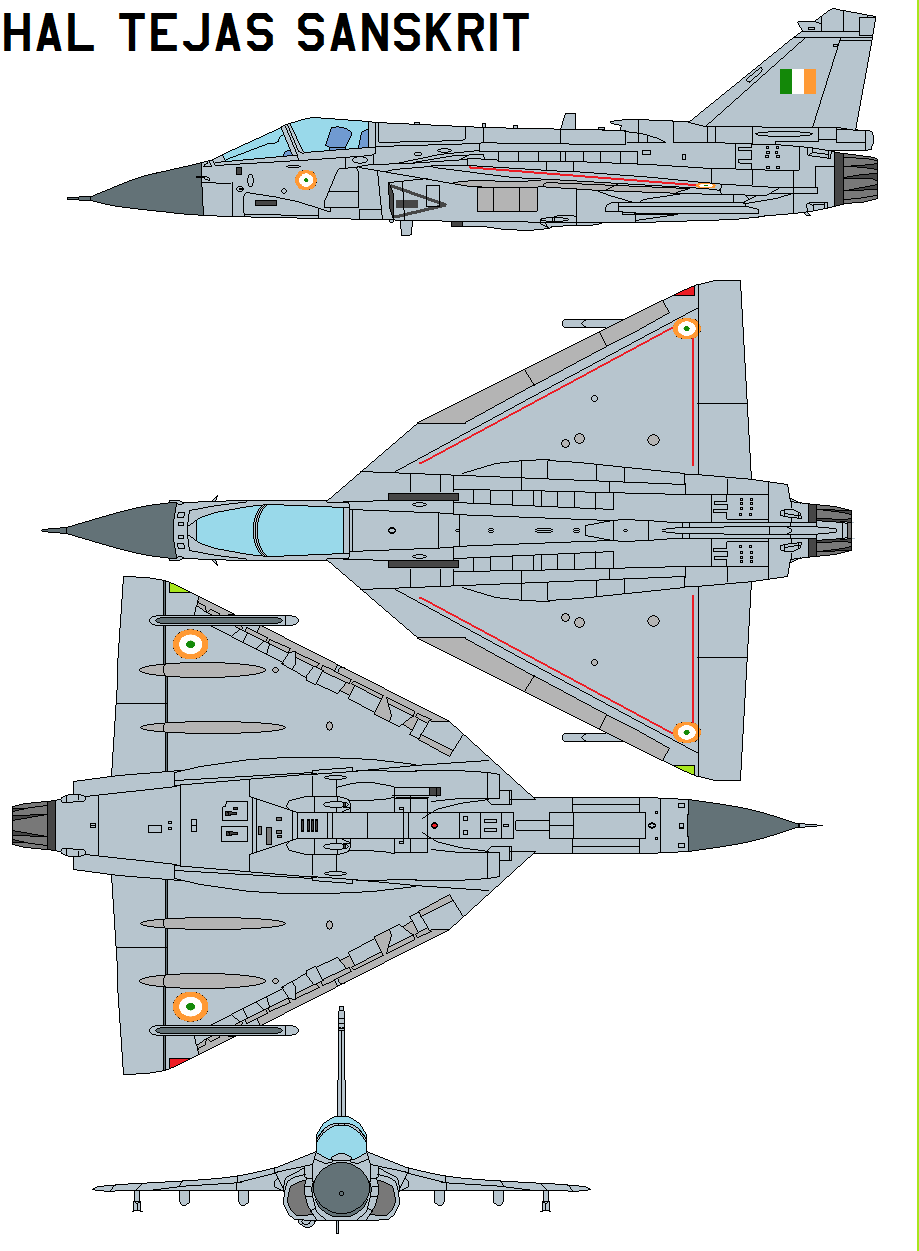
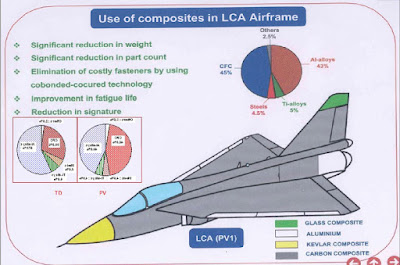
The tailless, compound-delta planform is designed to be small and lightweight.[97] This platform also minimises the control surfaces needed (no tailplanes or foreplanes, just a single vertical tailfin), permits carriage of a wider range of external stores, and confers better close-combat, high-speed, and high-alpha performance characteristics than comparable cruciform-wing designs. Extensive wind tunnel testing on scale models and complex computational fluid dynamics analyses have optimised the aerodynamic configuration of the LCA, giving it minimum supersonic drag, a low wing-loading, and high rates of roll and pitch.[96] Materials used included aluminium-lithium, superplastically formed titanium and carbon-fiber composite (CFC). Tejas employs CFC materials for up to 45 per cent of its airframe, including in the fuselage (doors and skins), wings (skin, spars and ribs), elevons, tailfin, rudder, air brakes and landing gear doors.[98] The wing and fin of the compound-delta aircraft are of carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer, and were designed to provide a minimum weight structure and to serve as integral fuel tanks.[99][100]
All weapons are carried on one or more of seven hardpoints with total capacity of greater than 4,000 kg: three stations under each wing and one on the under-fuselage centreline. An eighth offset station beneath the port-side intake trunk can carry a variety of pods like FLIR, IRST, laser rangefinder/designator, as can the centreline under-fuselage station and inboard pairs of wing stations.[33][101][102] Auxiliary fuel tanks of 800 and 1,200 liters can be carried under the fuselage to extend range. An aerial refuelling probe on the starboard side of the forward fuselage can further extend range and endurance.[103] Although two-seat variants of the LCA are planned, the examples built to date are crewed by a single pilot on a Martin-Baker zero-zero ejection seat. The British Martin-Baker ejection seat is planned to be replaced with a locally developed alternative.[104] Tejas requires a very short runway and "rockets off the runway and into the air in a mere 500 metres".[98]
Airframe
The LCA is constructed of aluminium-lithium alloys, carbon-fibre composites (C-FC), and titanium-alloy steels. The Tejas employs C-FC materials for up to 45% of its airframe by weight, including in the fuselage (doors and skins), wings (skin, spars and ribs), elevons, tailfin, rudder, air brakes and landing gear doors. Composites are used to make an aircraft both lighter and stronger at the same time compared to an all-metal design, and the LCA's percentage employment of C-FCs is one of the highest among contemporary aircraft of its class.[105] Apart from making the plane much lighter, there are also fewer joints or rivets, which increases the aircraft's reliability and lowers its susceptibility to structural fatigue cracks.[106] The tailfin is a monolithic honeycomb piece, reducing the manufacturing cost by 80% compared to the "subtractive" or "deductive" method, involving the carving out of a block of titanium alloy by a computerised numerically controlled machine. No other manufacturer is known to have made fins out of a single piece.[107]The use of composites in the LCA resulted in a 40% reduction in the total number of parts compared to using a metallic frame. Furthermore, the number of fasteners has been reduced by half in the composite structure from the 10,000 that would have been required in a metallic frame design. The composite design also helped to avoid about 2,000 holes being drilled into the airframe. Overall, the aircraft's weight is lowered by 21%. While each of these factors can reduce production costs, an additional benefit — and significant cost savings — is realised in the shorter time required to assemble the aircraft — seven months for the LCA as opposed to 11 months using an all-metal airframe.[108]
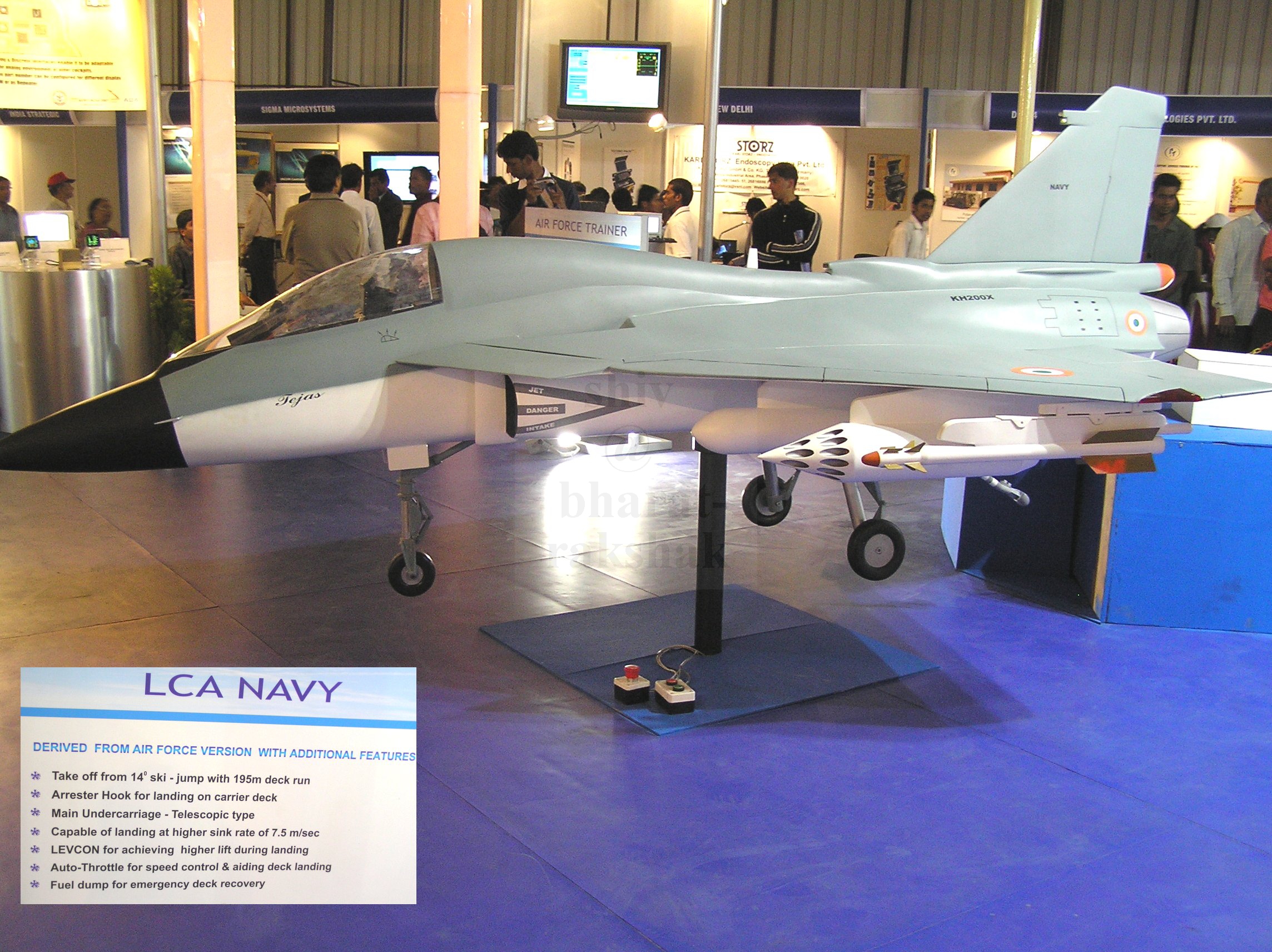
The airframe of the naval variant of the Tejas will be modified with a nose droop to provide improved view during landing approach, and wing leading edge vortex controllers (LEVCON) to increase lift during approach.[14] The LEVCONs are control surfaces that extend from the wing-root leading edge and thus afford better low-speed handling for the LCA, which would otherwise be slightly hampered due to the increased drag that results from its delta-wing design. As an added benefit, the LEVCONs will also increase controllability at high angles of attack (AoA).[109] The naval Tejas will also have a strengthened spine, a longer and stronger undercarriage, and powered nose wheel steering for deck manoeuvrability.[25][110] The Tejas trainer variant will have "aerodynamic commonality" with the two-seat naval aircraft design.[111]
Flight controls
Since the Tejas is a relaxed static stability design, it is equipped with a quadruplex digital fly-by-wire flight control system to ease pilot handling.[112] The Tejas aerodynamic configuration is based on a pure delta-wing layout with shoulder-mounted wings. Its control surfaces are all hydraulically actuated. The wing's outer leading edge incorporates three-section slats, while the inboard sections have additional slats to generate vortex lift over the inner wing and high-energy air-flow along the tail fin to enhance high-AoA stability and prevent departure from controlled flight. The wing trailing edge is occupied by two-segment elevons to provide pitch and roll control. The only empennage-mounted control surfaces are the single-piece rudder and two airbrakes located in the upper rear part of the fuselage, one each on either side of the fin.[113]The digital FBW system of the Tejas employs a powerful digital flight control computer (DFCC) made by Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) comprising four computing channels, each with its own independent power supply and all housed in a single LRU. The DFCC receives signals from a variety of sensors and pilot control stick inputs, and processes these through the appropriate channels to excite and control the elevons, rudder and leading edge slat hydraulic actuators. The DFCC channels are built around 32-bit microprocessors and use a subset of the Ada programming language for software implementation. The computer interfaces with pilot display elements like the MFDs through MIL-STD-1553B multiplex avionics data buses and RS-422 serial links.[98][114][115] in-flight refuelling capability via retractable probes on the aircraft's starboard side, and an on-board oxygen-generating system for longer missions.
Propulsion

General Electric F404-IN20 engine for the eight pre-production LSP aircraft and two naval prototypes
The original plan was for the LCA prototype aircraft to be equipped with the General Electric F404-GE-F2J3 afterburning turbofan engine, while the production aircraft would be fitted with the indigenous GTRE GTX-35VS Kaveri turbofan being developed in a parallel. Continued development snags with the Kaveri resulted in a 2003 decision to procure the upgraded GE F404-IN20 engine for the eight pre-production LSP aircraft and two naval prototypes and after accelerated trials an order was placed for 24 more IN20 engines for installation on the first 20 production aircraft. The Tejas Mark II will be equipped with the more powerful GE F414engine.[89][98][116]
Avionics
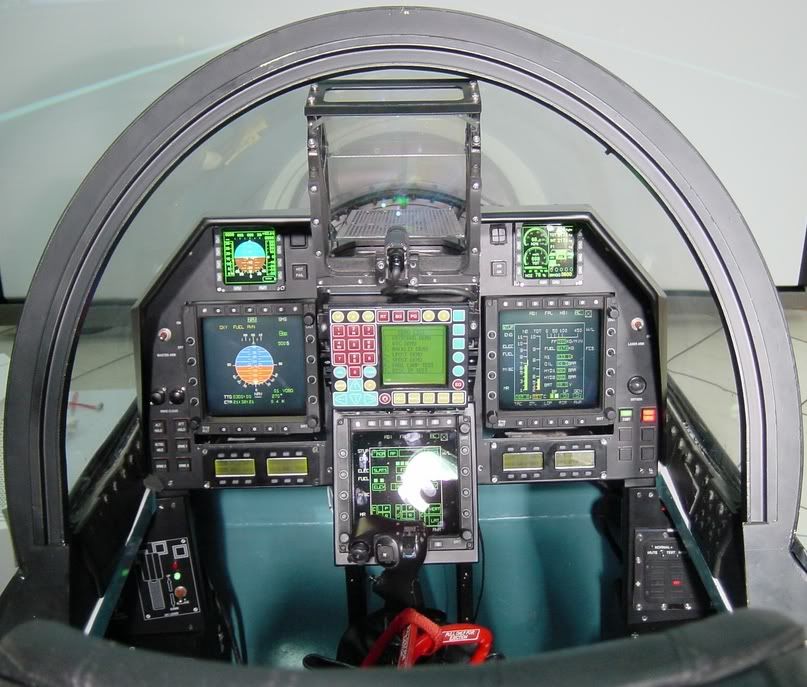
The Tejas has a night vision goggles (NVG)-compatible "glass cockpit" that is dominated by an CSIR-CSIO developed indigenous head-up display (HUD), three 5 in x 5 in multi-function displays, two Smart Standby Display Units (SSDU), and a "get-you-home" panel providing the pilot with essential flight information in case of an emergency. The displays provide information on the key flight systems and controls on a need-to-know basis, along with basic flight and tactical data. The pilot interacts with onboard systems through a multifunctional keyboard and several selection panels.[98] The CSIO-developed HUD, Elbit-furnished DASH helmet-mounted display and sight (HMDS),[118] and hands-on-throttle-and-stick (HOTAS) controls reduce pilot workload and increase situation awareness by allowing the pilot to access navigation and weapon-aiming information with minimal need to spend time "head down" in the cockpit.[101][119]The Tejas is equipped with both GPS and a ring laser gyro based inertial navigation system; for flying in poor conditions, an Instrument Landing System (ILS) and a ground proximity warning system based on the Terrain Referenced Navigation (TRN) system is also employed.[102][120][121] The LCA also has secure and jam-resistant communication systems such as the IFF transponder/interrogator, VHF/UHF radios, and air-to-air/air-to-ground datalinks. The ADA Systems Directorate's Integrated Digital Avionics Suite (IDAS) integrates the flight controls, environmental controls, aircraft utilities systems management, stores management system (SMS), etc. on three 1553B buses by a centralised 32-bit, high-throughput mission computer.[101]
Radar and sensors
The pulse-doppler Multi-Mode Radar is designed to keep track of a maximum of 10 targets and allows simultaneous multiple-target engagement. Jointly developed by the LRDE and HAL Hyderabad, the MMR is to perform multi-target search, track-while-scan(TWS), and ground-mapping functions.[116][122][123] It features look-up/look-down modes, low/medium/high pulse repetition frequencies (PRF), platform motion compensation, doppler beam-sharpening, moving target indication(MTI), Doppler filtering, constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detection, range-Doppler ambiguity resolution, scan conversion, and online diagnostics to identify faulty processor modules.[119]While originally planned to be fitted on the initial production aircraft, delays in the MMR's development prompted the DRDO to co-operate with Israel Aerospace Industries to integrate a hybrid version of the EL/M-2032 radar on the Tejas.[63] The EL/M-2032 radar used in LSP-3 has a detection and tracking range of up to 150 km in air-to-air mode, the air-to-ground mode generates high resolution radar imagery of locations at up to 150 km, and air-to-sea mode can detect and classify naval targets at ranges of up to 300 km.[98] The development of an active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar is expected to begin pending the selection of a developmental partners between DRDO foreign partners ; prospective partners include Europe's Airbus Group and Israel's Elta. The initial contract is to involve the co-development of 10 prototypes.[124]
Tejas is also to be equippable with an Infra-red search and track (IRST) sensor, which can detect and track thermal energy emissions.[98][125] This system shall be pod-based, additional sensor pods are to include a Drop tanks for ferry flight/extended range/loitering time,FLIR targeting pod, ECM pods, Flares/Infrared decoys dispenser pod and chaff pod, EO/IR sensor pod, LITENING targeting pods Forward looking infrared (FLIR)sensor, and a laser rangefinder/designator, which can be used in various capacities, including reconnaissance, training, or attack.[33][101][102]
Self-protection
The electronic warfare suite is designed to enhance the survivability during deep penetration and combat. The LCA's EW suite is developed by the Defence Avionics Research Establishment (DARE) with support from the Defence Electronics Research Laboratory (DLRL). This EW suite, known as Mayavi, includes a radar warning receiver (RWR), Missile Approach Warning (MAW) and a Laser warning receiver (LWR) system, Infrared & Ultraviolet Missile warning sensors, self-protection jammer, chaff, jaff and flares dispenser. an electronic countermeasures (ECM) suite and a towed radar decoy (TRD).In the interim, the Indian Ministry of Defense has revealed that an unspecified number of EW suites had been purchased from Israel's Elisra for the LCA prototypes.[120][121][126]Stealth features have been designed into Tejas.[127] Being very small, there is an inherent degree of visual stealth, but the airframe use of a high degree of composites (which do not reflect radar waves), a Y-duct inlet which shields the engine compressor face from probing radar waves, and the application of radar-absorbent material (RAM) coatings are intended to minimise its susceptibility to detection and tracking by the radars of enemy fighters.[119]
Operational history
The work to raise the first squadron started in July 2011. The Tejas will be inducted into the 45th squadron, the Flying Daggers and will be based in Bangalore before being moved to Sulur.[128] The squadron will initially consist of four aircraft SP-3 to SP-6. The IAF's Aircraft & Systems Testing Establishment will receive four aircraft already built, the SP-1 and 2 and LSP-7 and 8.[129]The Final Operational Clearance (FOC) campaign began in December 2013, with three aircraft from Tejas flight-line successfully completing advanced weapon trials. The campaign was held in Jamnagar. New weapons were integrated on the aircraft.[130] As part of the FOC, aircraft is being readied for all-weather trials in Bangalore. "One aircraft is also being readied for night flying with upgraded systems and software. Plans are afoot to take Tejas for hot weather trials in Gwalior next month," the trials official added. Tejas had taken its maiden flight on 4 January 2001, and as of December 2013, it had completed 2,587 sorties covering over 1,750 hours.[130]
Variants
Prototypes
Aircraft already built and projected models to be built. Model designations, tail numbers and dates of first flight are shown.- Technology Demonstrators (TD)
- TD-1 (KH2001) – 4 Jan 2001
- TD-2 (KH2002) – 6 June 2002
- Prototype Vehicles (PV)
- PV-1 (KH2003) – 25 November 2003
- PV-2 (KH2004) – 1 December 2005
- PV-3 (KH2005) – 1 December 2006. This is the production variant.
- PV-4
- PV-5 (KH-T2009) – 26 November 2009 – Fighter/Trainer Variant
- Naval Prototypes (NP)
- NP-1 – Two-seat Naval variant for carrier operations. Rolled out in July 2010.[131] NP-1 made its first flight on 27 April 2012.[80]
- NP-2 – Single-seat LCA MK 1 Naval variant for carrier operations. Both NP-1 & NP-2 are powered by GE-404 engine.[80]
- NP-3 & NP-4 – Single-seat LCA MK 2 Naval variant for carrier operations to be powered by the GE-414 engines. The design work on the two aircraft is nearly complete.[80]
- NP-5 – Another Single-seat LCA MK 1 Naval variant is planned so as to enhance the pace of certification process for Naval LCA.[80]
- Limited Series Production (LSP) aircraft
- LSP-1 (KH2011) – 25 April 2007. This LCA is powered by F404-F2J3 Engine.[132]
- LSP-2 (KH2012) – 16 June 2008. This is the first LCA fitted with F404-IN20 engine.[132]
- LSP-3 23 April 2010. The first aircraft to have the Hybrid MMR radar[63] and will be close to the IOC standard.
- LSP-4 (KH2014) – 2 June 2010. The first aircraft that was flown in the configuration that will be delivered to the Indian Air Force.[64] In addition to the Hybrid MMR, the aircraft flew with a Countermeasure Dispensing System and an identify friend or foe electronic system.[133]
- LSP-5 (KH2015) – 19 November 2010. IOC standard, with all sensors including night lighting in the cockpit, and an auto-pilot.[134]
- LSP-6 – Will be used to increase the Angle of Attack.[135] As well as develop better (Experimental) RAM coating to further reduce its radar signature.[136]
- LSP-7 (KH2017) – 9 March 2012. APU intake has been aerodynamically reshaped.
- LSP-8 – First flight trial completed in March 2013. LSP 8 is the version that will go for production.[85]
- SP-1 to SP-40 – Planned to fly by late 2013. The SP-1 and SP-2 will be part of No. 45 Squadron (Flying Daggers) that will be based initially in Bangalore, Karnataka.[136]
Planned production variants
- Tejas Trainer – Two-seat operational conversion trainer for the Indian Air Force.
- Tejas Navy – Twin- and single-seat carrier-capable variants for the Indian Navy. The LCA's naval variant is to be ready for carrier trials by 2013 and is slated for deployment on the INS Vikramaditya as well as the Vikrant class aircraft carrier.[137] It will be equipped for carrier operation with ski-jump take-off and arrested landing. It will include strengthened airframe and landing gear and the nose is drooped for better cockpit vision.[138]
Tejas Mark 2
Featuring the more powerful General Electric F414-GE-INS6 engine with 98 kN of thrust and refined aerodynamics, the Mark 2 is being developed to meet the Indian Air Force requirements and will incorporate 5th generation fighter elements which are intended to make way into the FGFA and AMCA. The Tejas Mk 2 will now have a length of 14.2 metres (1-metre more than that of the Tejas Mk 1, for incorporating a stretched nose section and a modified fuselage section aft of the cockpit for housing an expanded complement of mission avionics LRUs), height of 4.6 metres (as opposed to 4.4 metres of the Tejas Mk 1, to accommodate an enlarged vertical tail-section) and a wingspan of 8.2 metres, same as that of the Tejas Mk 1, that, however with an increased wing area. External stores capacity will be boosted to 5,000 kg (as opposed to 4,000 kg for the Tejas Mk1), while the twin internal air-intake ducts will be minimally enlarged to cater to the increased airflow requirements of the 98 kN thrust F414-GE-INS6 turbofan built by GE Aero Engines. The Ministry of Defence had, last January, sanctioned US$542.44 million (Rs 2,431.55-crore) for ADA to develop the IAF's Tejas Mk 2 variant and the Indian Navy's LCA Mk 2 (Navy) variant. The IAF is committed to procuring an initial 83 Tejas Mk 2s and the Indian Navy has expressed its firm requirement for 46 LCA Mk2 (Navy).[58][139][140]Tejas Mark 3
Tejas Mark 3 is a planned version. It is to be stealthier than Mark 2 and have composite usage up to 70 percent of the aircraft. The aircraft is to be powered by Kaveri engine once the development of the engine is completed. It is to also feature reduced heat signature.[141]Operators
- Indian Air Force – 40 LCA Mk 1 aircraft plus 8 Limited Series Production (LSP) aircraft on order. Plans to order 6 squadrons of LCA Mk 1 and 4 squadrons of LCA Mk 2 aircraft after completing production of LCA Mk 1.[142][143][144] The IAF was considering at least 14 Tejas squadrons with 294 aircraft as of February 2014, with each squadron to have 21 aircraft.[145]
- Indian Navy – Signed an order for six Naval LCAs at an approximate cost of US$31.09 million per aircraft.[146] The Indian Navy has a requirement for 40 Tejas aircraft.[69][144]
Specifications (HAL Tejas Mk.1)
- Crew: 1
- Length: 13.20 m (43 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 8.20 m (26 ft 11 in)
- Height: 4.40 m (14 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 38.4 m² (413 ft²)
- Empty weight: 6,500 kg (14,300 lb)
- Loaded weight: 9,500 kg[147] (20,944 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 13,200 kg[147] (29,100 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × F404-GE-IN20 turbofan
- Dry thrust: 53.9 kN[150] (12,100 lbf)
- Thrust with afterburner: 89.8 kN (20,200 lbf[151])
- Internal fuel capacity: 2,458 kg
- External fuel capacity: 2 x 1,200-litre drop tank at inboard, 1 x 725-litre drop tank under fuselage
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.6 (1,350 km/h) calibrated airspeed (CAS) at high altitude, reached in testing of IOC-I,[147] theoretically capable of Mach 1.8[152]
- Range: 850 km[153] (459 nmi, 528 mi)
- Combat radius: 1300 km[153] (162 nmi, 186 mi)
- Ferry range: 3,000 km, Theoretically capable of 3,500 km[101] (1,840 mi)
- Service ceiling: 15,000 m[147] (49,200 ft, possibility of being raised to 60,000 ft)
- Wing loading: 247 kg/m² (50.7 lb/ft²)
- Thrust/weight: 1.07[147]
- g-limits: +8/−3.5 g[147]
- Guns: 1× mounted 23 mm twin-barrel GSh-23 cannon with 220 rounds of ammunition.
- Hardpoints: 8 total: 1× beneath the port-side intake trunk for targeting pods, 6× under-wing, and 1× under-fuselage with a capacity of 4,200 kg external fuel and ordnance
- Missiles:
- Air-to-air missiles:
- Air-to-surface missiles:
- Anti-ship missiles
- Bombs:
Source:[154]- KAB-1500L laser-guided bombs
- GBU-16 Paveway II
- FAB-250
- ODAB-500PM fuel-air explosives
- ZAB-250/350 incendiary bombs
- BetAB-500Shp powered concrete-piercing bombs
- FAB-500T dumb bombs
- OFAB-250-270 dumb bombs
- OFAB-100-120 dumb bombs
- RBK-500 cluster bomb stake
- Others:[154]
- S-8 rocket pods
- Bofors 135 mm rocket
- Drop tanks for ferry flight/extended range/loitering time.
- LITENING targeting pod[155][156]
















No comments:
Post a Comment