From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| T-38 Talon | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| A USAF T-38A Talon from 560th Flying Training Squadron, Randolph Air Force Base Texas, flying over the Texas countryside in 2001 | |
| Role | Advanced trainer |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Northrop Corporation |
| First flight | 10 March 1959 |
| Introduction | 17 March 1961 |
| Retired | Portuguese Air Force 1993 |
| Status | Operational |
| Primary users | United States Air Force United States Navy NASA Turkish Air Force |
| Produced | 1961–1972 |
| Number built | 1,146 |
| Unit cost | |
| Developed from | Northrop N-156 |
| Variants | Northrop F-5 |

Two T-38 Talon chase planes follow Space Shuttle Columbia as it lands at Northrop Strip in White Sands, New Mexico, ending its mission STS-3.
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the largest operator of the T-38. In addition to training USAF pilots, the T-38 is used by NASA. The US Naval Test Pilot School is the principal US Navy operator (other T-38s were previously used as USN aggressor aircraft until replaced by the similar Northrop F-5 Tiger II). Pilots of other NATO nations fly the T-38 in joint training programs with USAF pilots.
As of 2014, the T-38 has been in service for over 50 years with its original operator (the USAF).
Contents
Design and development
The basic airframe was used for the light combat aircraft F-5 Freedom Fighter family. In the 1950s Northrop began studying lightweight and more affordable fighter designs. The company began with its single-engined Northrop N-102 Fang concept.[1] The N-102 was facing weight and cost growth, so the project was canceled and the company N-156 project was begun.[2]Although the USAF had no need for a small fighter at the time, it became interested in the trainer as a replacement for the T-33 Shooting Star it was then using in that role. The first of three prototypes (designated YT-38) flew on 10 March 1959.[3] The type was quickly adopted and the first production examples were delivered in 1961, officially entering service on 17 March that year, complementing the T-37 primary jet trainer. When production ended in 1972, 1,187 T-38s had been built (plus two N-156T prototypes). Since its introduction, it is estimated that some 50,000 military pilots have trained on this aircraft. The USAF remains one of the few armed flying forces using dedicated supersonic final trainers, as most, such as the US Navy, use high subsonic trainers.[4]
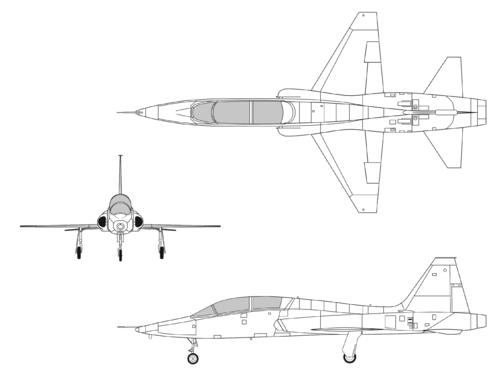
The T-38 is of conventional configuration, with a small, low, long-chord wing, a single vertical stabilizer, and tricycle undercarriage. The aircraft seats a student pilot and instructor in tandem, and has intakes for its two turbojet engines at the wing roots. Its nimble performance has earned it the nickname white rocket. In 1962 the T-38 set absolute time-to-climb records for 3000, 6000, 9000 and 12000 meters, beating the records for those altitudes set by the F-104 in December 1958. (The F-4 beat the T-38's records less than a month later.)
The F-5B and F (which also derive from the N-156) can be distinguished from the T-38 by the wings; the wing of the T-38 meets the fuselage straight and ends square, while the F-5 has leading edge extensions near the wing roots and wingtip launch rails for air to air missiles. Under the paint the T-38 wing is constructed of honeycomb material while the wing of the F-5 family uses conventional skin over underlying support structure.
Most T-38s built were of the T-38A variant, but the USAF also had a small number of aircraft that had been converted for weapons training. These aircraft (designated AT-38B) had been fitted with a gunsight and could carry a gunpod, rockets, or bombs on a centerline pylon. In 2003, 562 T-38s were still operational with the USAF and are currently undergoing structural and avionics programs (T-38C) to extend their service life to 2020. Improvements include the addition of a HUD, GPS, INS (Inertial Navigation System), and TCAS as well as PMP (a propulsion modification to improve low-altitude engine thrust). Many USAF variants (T-38A and AT-38B) are being converted to the T-38C.
The fighter version of the N-156 was eventually selected for the US Military Assistance Program and produced as the F-5 Freedom Fighter. Many of these have since reverted to a weapons training role as various air forces have introduced newer types into service. The F-5G was an advanced single-engined variant later renamed the F-20 Tigershark.
Operational history
Military
The USAF Strategic Air Command (SAC) had T-38 Talons in service from 1978 until SAC's inactivation in 1991. These aircraft were used to enhance the career development of bomber copilots through the "Accelerated Copilot Enrichment Program." They were later used as proficiency aircraft for all B-52 and B-1 pilots, as well as Lockheed SR-71, U-2, Boeing KC-135, and KC-10 pilots. SAC's successors, the Air Combat Command (ACC) and the Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC), continue to retain T-38s as proficiency aircraft for U-2 pilots and B-2 pilots, respectively.[4]The Air Training Command's (ATC) successor, the Air Education and Training Command (AETC), uses the T-38C to prepare pilots for aircraft such as the F-15C Eagle and F-15E Strike Eagle, as well as the F-16 Fighting Falcon, B-52 Stratofortress, B-1B Lancer, B-2 Spirit, A-10 Thunderbolt, F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II. The AETC received T-38Cs in 2001 as part of the Avionics Upgrade Program. The T-38Cs owned by the AETC have undergone propulsion modernization which replaces major engine components to enhance reliability and maintainability, and an engine inlet/injector modification to increase available takeoff thrust.[4] These upgrades and modifications, with the Pacer Classic program, should extend the service life of T-38s past 2020.
Besides the USAF, USN and NASA, other T-38 operators include the German Air Force (Luftwaffe), the Portuguese Air Force, the Republic of China Air Force, and the Turkish Air Force.[4]
NASA
NASA operates a fleet of 32 T-38 aircraft[5] and uses the aircraft as a jet trainer for its astronauts, as well as a chase plane. Its fleet is housed primarily at Ellington Field in Houston, Texas. NASA's internal projections show the number of operational jet trainers falling to 16 by 2015. The agency spends between $25 million and $30 million annually to fly and maintain the T-38s.[6]Accidents
NASA's T-38s were involved in four separate fatal accidents in the 1960s and 1970s, and several non-fatal incidents.- 1964 Oct 31: Astronaut Theodore Freeman was killed as a result of a bird strike.[7][8]
- 1966 February 28 (1966 NASA T-38 crash): Astronauts Elliot See and Charles Bassett were killed when they struck a building in fog.[9][10]
- 1967 October 5: Astronaut Clifton "C.C." Williams was killed in a crash due to an aileron jam.[11][12]
- 1972 Jan 20: NASA pilot Stewart M. Present and NASA pilot Mark C. Heath were killed when they crashed during an instrument approach in fog.[13]
Two fatal crashes in 2008, one on 23 April at Columbus Air Force Base in Mississippi and the second on 1 May at Sheppard Air Force Base in Wichita Falls, Texas, resulted in four fatalities, causing the Air Force to temporarily ground the aircraft.[14] On 21 May 2009, a T-38 crashed just north of Edwards Air Force Base in the Mojave Desert.[15]
Replacement
The T-X Program has been established to enable the United States Air Force to buy a new two-seat jet trainer for fast-jet training to replace the T-38. Aviation Week & Space Technology reporters wrote in 2010 "there appears to be no rush to purchase T-38 replacements"; "the service is conducting an analysis of alternatives" with results "not expected to be ready until the Fiscal 2013 budget".[16] In subsequent years, the Air Force indicated it would launch a competition for the T-38's replacement. Likely bidders include: A partnership of BAE Systems and Rolls Royce, offering the Hawk trainer, equipped with Rolls' Adour Mk951 engine offering 6,500 lb of thrust and FADEC; Lockheed Martin and Korea Aerospace Industries, offering the T-50; and General Dynamics and Alenia Aermacchi offering the M-346, an aircraft whose design originated with the Russian Yak-130.[17]Civil
There are seven privately owned T-38s in the U.S.[5] Boeing owns two T-38s, which it uses as chase planes.[5] Thornton Corporation owns two T-38s and three F-5s and the National Test Pilot School owns one T-38.[5] In addition, ILOAJP HOLDING and Wayne L. Siltanen own one each.[5]Variants
- N-156T : Northrop company designation.
- YT-38 : Prototypes, two built with YJ85-GE-1 engines, later designated YT-38A and four pre-production aircraft with YJ-85-GE-5 engines, later designated T-38A.[18]
- T-38A : Two-seat advanced training aircraft, production model, 1,139 built.[18]
- T-38A(N) : Two-seat astronaut training version for NASA.
- AT-38A : A small number of T-38As were converted into weapons training aircraft.
- DT-38A : A number of US Navy T-38As were converted into drone directors.
- NT-38A : A small number of T-38As were converted into research and test aircraft.
- QT-38A : Unmanned target drone aircraft.
- AT-38B : Two-seat weapons training aircraft.
- T-38C : A T-38A with structural and avionics upgrades.[4]
- T-38M : Modernized Turkish Air Force T-38As with full glass cockpit and avionics, upgraded by Turkish Aerospace Industries under the project codename "ARI" (Turkish: Arı, for Bee).[19]
- N-205 : "Space trainer" variant proposed in May 1958, with triple rocket engines for vertical launch.[20][21] Capable of Mach 3.2 on its way to an altitude of 200,000 feet (61,000 m).
- ST-38 or N-205B : Revised proposal in April 1963 for the new Aerospace Research Pilot School, with a rolling takeoff, top speed of Mach 3.3 and a ceiling of 285,000 feet (87,000 m), high enough to qualify its pilots for astronaut wings.
- T-38 VTOL Proposed vertical takeoff variant with four lift nozzles behind the pilot.
Operators
- The German Air Force has 35 in use as of January 2009.[22]
- Republic of China Air Force has 40 in operation as of January 2009.[22]
- Turkish Air Force has 67 T-38M in use as of November 2008.[23]
- United States Air Force has 459 T-38 trainers in service as of September 2008.[24]
- United States Air Force Thunderbirds – eight aircraft for aerobatic demonstrations (1974–1982)
- United States Navy has ten aircraft in use as November 2008.[23]
- NASA (~32 aircraft)
Former Operators
- Portuguese Air Force received 12 aircraft in 1977. Initially operated by 201 Sqn. "Falcões" (Falcons) at Air Base No. 5, in 1980 they were transferred to 103 Sqn. "Caracóis" (Snails) being stationed in Air Base No. 11. They were finally retired in 1993.
- Republic of Korea Air Force leased a total of 30 T-38A from the United States in April 1999. All units were returned to the United States by 2009 after near completion of production of T-50 Golden Eagle supersonic trainer.
Aircraft on display
- T-38A
- 59-1602 – United States Air Force Academy, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Painted as "Thunderbird 1"
- 60-0549 – Prairie Aviation Museum, in Bloomington, Illinois[25]
- 60-0593 – March Field Air Museum at March ARB (former March AFB) in Riverside, California. It is on display in Thunderbirds markings.[26]
- 61-0817 – Oklahoma Welcome Station, near Tinker AFB, Oklahoma.[27]
- 61-0824 – Hill Aerospace Museum near Hill AFB in Utah.[28]
- 61-0854 – Pima Air and Space Museum, adjacent to Davis-Monthan AFB in Tucson, Arizona. It is on display in the markings of the 479th Tactical Training Wing at Holloman AFB, NM, circa 1982.[29]
- 61-0902 – Science Spectrum in Lubbock, Texas.[30]
- 63-8224 – Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum in McMinnville, Oregon. It is painted in NASA colors suspended from the ceiling in their Air and Space Exhibit Hall.[31]
- YT-38A
- 58-1192 – South Dakota Air and Space Museum at Ellsworth AFB in South Dakota.[32]
- AT-38B
- 60-0576 – Holloman AFB, New Mexico.[33]
- 65-10441 – National Museum of the United States Air Force at Wright-Patterson AFB in Dayton, Ohio. This aircraft was retired in 1991, came to the museum in 1999, and placed on display in 2004.[34]
Specifications (T-38A)
Data from USAF factsheet[4]
General characteristics- Crew: two: student and instructor
- Length: 46 ft 4.5 in (14.14 m)
- Wingspan: 25 ft 3 in (7.7 m)
- Height: 12 ft 10.5 in (3.92 m)
- Wing area: 170 ft² (16 m²)
- Empty weight: 7,200 lb (3,270 kg)
- Loaded weight: 11,820 lb (5,360 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 12,093 lb (5,485 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × General Electric J85-5A (J85-5R after PMP modification) afterburning turbojets
- Dry thrust: 2,050 lb (9.1 kN) each
- Thrust with afterburner: 3,850 lbf (17.1 kN) each
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.3 (858 mph, 1,381 km/h)
- Range: 1,140 mi (1,835 km)
- Service ceiling: 50,000 ft (15,240 m)
- Rate of climb: 33,600 ft/min (170.7 m/s)
- Wing loading: 70 lb/ft² (340 kg/m²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.65
See also
- Related development
- Related lists









No comments:
Post a Comment